TAMRA NHS ester, 5-isomer
| Cat. # | Quantity | Price | Lead time | Buy this product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17120 | 1 mg |
–
|
in stock | |
| 27120 | 5 mg |
$210
|
in stock | |
| 47120 | 25 mg |
$350
|
5 days | |
| 57120 | 50 mg |
$595
|
in stock | |
| 67120 | 100 mg |
$790
|
in stock |

TAMRA (tetramethylrhodamine) is a xanthene dye of rhodamine series. This fluorophore has been used for quite a long time for the preparation of dual-labeled qPCR TaqMan oligonucleotide probes containing TAMRA and fluorescein (FAM).
Like many other xanthene fluorophores, TAMRA is available as two isomers (5- and 6-isomer) with nearly identical optical properties. This product is an isomerically pure 5-TAMRA.
TAMRA NHS is an amine-reactive reagent. It can be used to label proteins, peptides, and modified oligonucleotides containing amine groups.
Absorption and emission spectra of 5-TAMRA

Customers also purchased with this product
General properties
| Appearance: | dark colored solid |
| Molecular weight: | 527.53 |
| CAS number: | 321862-17-3 |
| Molecular formula: | C29H25N3O7 |
| IUPAC name: | (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 3',6'-bis(dimethylamino)-3-oxospiro[2-benzofuran-1,9'-xanthene]-5-carboxylate |
| Solubility: | good in DMF, DMSO, low in water |
| Quality control: | NMR 1H, HPLC-MS (95%) |
| Storage conditions: | Storage: 12 months after receipt at -20°C in the dark. Transportation: at room temperature for up to 3 weeks. Avoid prolonged exposure to light. Desiccate. |
| MSDS: | Download |
| Product specifications |
Spectral properties
| Excitation/absorption maximum, nm: | 541 |
| ε, L⋅mol−1⋅cm−1: | 84000 |
| Emission maximum, nm: | 567 |
| Fluorescence quantum yield: | 0.1 |
| CF260: | 0.32 |
| CF280: | 0.19 |
Product citations
- Sokolov, A. V.; Isakova-Sivak, I. N.; Mezhenskaya, D. A.; Kostevich, V. A.; Gorbunov, N. P.; Elizarova, A. Yu.; Matyushenko, V. A.; Berson, Yu. M.; Grudinina, N. A.; Kolmakov, N. N.; Zabrodskaya, Y. A.; Komlev, A. S.; Semak, I. V.; Budevich, A. I.; Rudenko, L. G.; Vasilyev, V. B. Molecular Mimicry of the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: From the Interaction of Spike-Specific Antibodies with Transferrin and Lactoferrin to the Antiviral Effects of Human Recombinant Lactoferrin. Biometals, 2023, 36(3), 437–462. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00458-6
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Z. Chemically-Modified Sepharose 6B Beads for Collection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Biomolecules, 2023, 13(7), 1071. doi: 10.3390/biom13071071
- Bresinsky, M.; Shahraki, A.; Kolb, P.; Pockes, S.; Schihada, H. Development of Fluorescent AF64394 Analogues Enables Real-Time Binding Studies for the Orphan Class A GPCR GPR3. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2023, 66(21), 15025-15041. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01707
- Alexandrova, V. V.; Anisimov, M. N.; Zaitsev, A. V.; Mustyatsa, V. V.; Popov, V. V.; Ataullakhanov, F. I.; Gudimchuk, N. B. Theory of Tip Structure–Dependent Microtubule Catastrophes and Damage-Induced Microtubule Rescues. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2022, 119(46), e2208294119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208294119






















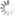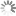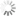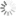
 $
$ 
